How a Hybrid Cars Work
We are all familiar with gasoline-powered cars, and most people have heard about or seen electric cars. A hybrid car is a combination of the two. A hybrid vehicle contains parts of both gasoline and electric vehicles in an attempt to get the best of both worlds.
The best way to understand the advantages of a hybrid vehicle is to think about a car traveling down a highway at the posted speed on level ground. In this case, the engine is doing three things:
The best way to understand the advantages of a hybrid vehicle is to think about a car traveling down a highway at the posted speed on level ground. In this case, the engine is doing three things:
- It is overcoming rolling resistance in the drive train.
- It is overcoming air resistance.
- It is powering accessories like the alternator, the power steering pump and the air conditioner.
The engine might need to produce no more than 10 or 20 horsepower (HP) to carry this load. The reason why cars have 100- or 200-horsepower engines to is handle acceleration from a standing stop, as well as for passing and hill climbing. We only use the maximum HP rating for 1% of our driving time. The rest of the time, we are carrying around the weight and the friction of the much larger engine, which wastes a lot of energy.
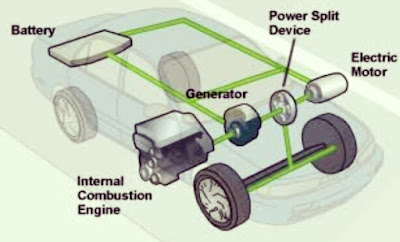
In a traditional hybrid vehicle, you have a complete electric car. It includes an electric motor to provide all of the power to the wheels, as well as batteries to supply the motor with electricity. Then you have a completely separate gasoline engine powering a generator. The engine is very small -- perhaps 10 to 20 horsepower -- and it is designed to run at just one speed for maximum efficiency. The purpose of this small, efficient engine is to provide enough power for the car at its cruising speed. During times of acceleration, the batteries provide the extra power necessary. When the car is decelerating or standing still, the batteries recharge. This sort of hybrid car is essentially an electric car with a built-in recharger for longer range. The advantage is that the small, efficient gasoline engine gets great mileage.
In a traditional hybrid vehicle, you have a complete electric car. It includes an electric motor to provide all of the power to the wheels, as well as batteries to supply the motor with electricity. Then you have a completely separate gasoline engine powering a generator. The engine is very small -- perhaps 10 to 20 horsepower -- and it is designed to run at just one speed for maximum efficiency. The purpose of this small, efficient engine is to provide enough power for the car at its cruising speed. During times of acceleration, the batteries provide the extra power necessary. When the car is decelerating or standing still, the batteries recharge. This sort of hybrid car is essentially an electric car with a built-in recharger for longer range. The advantage is that the small, efficient gasoline engine gets great mileage.